INTRODUCTION TO WELDING METALLURGY
Metallurgy is one of the main subjects in materials technology, besides ceramic, polymer, semiconductor, etc. Through this subject, students will be exposed to the phase transformation in metal and the relationship between the effect of heat treatment, metal alloying and carbon content (for the case of iron steel) to the formation of microstructure as well as its mechanical property.
During heat treatment, metal is heated to a certain temperature and cooled to room temperature. In some cases, the metal is hold at the temperature for a specific duration, depending on the purpose of heat treatment.
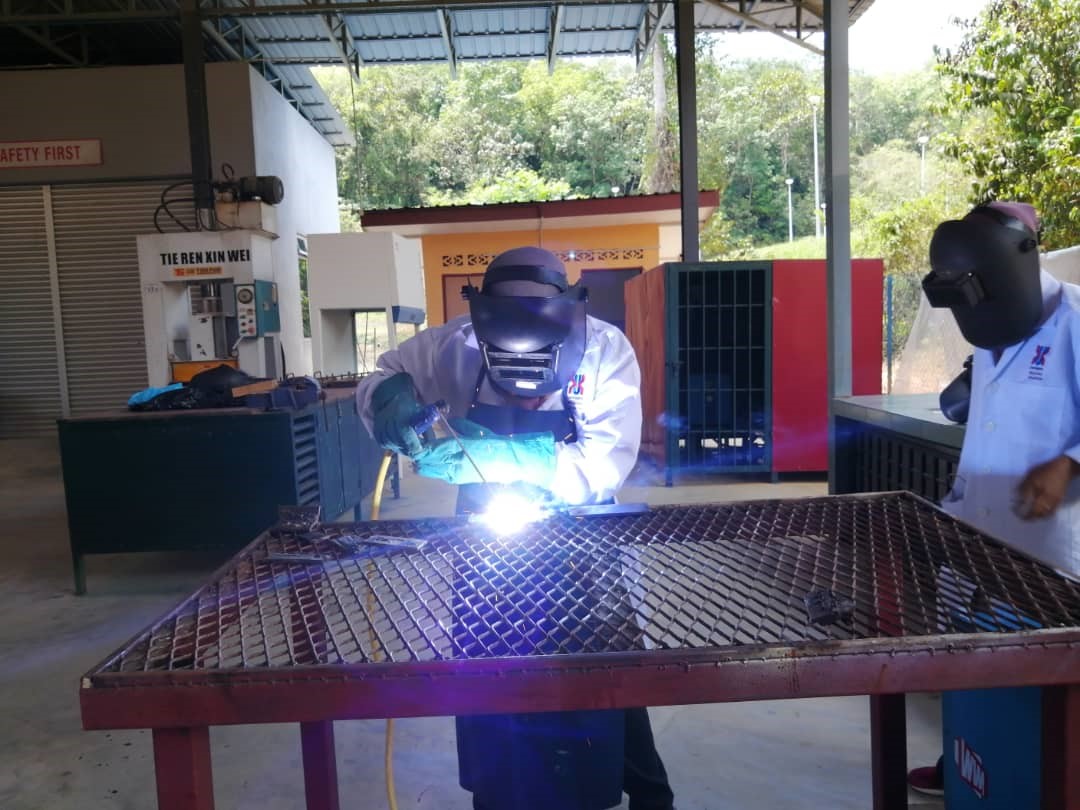
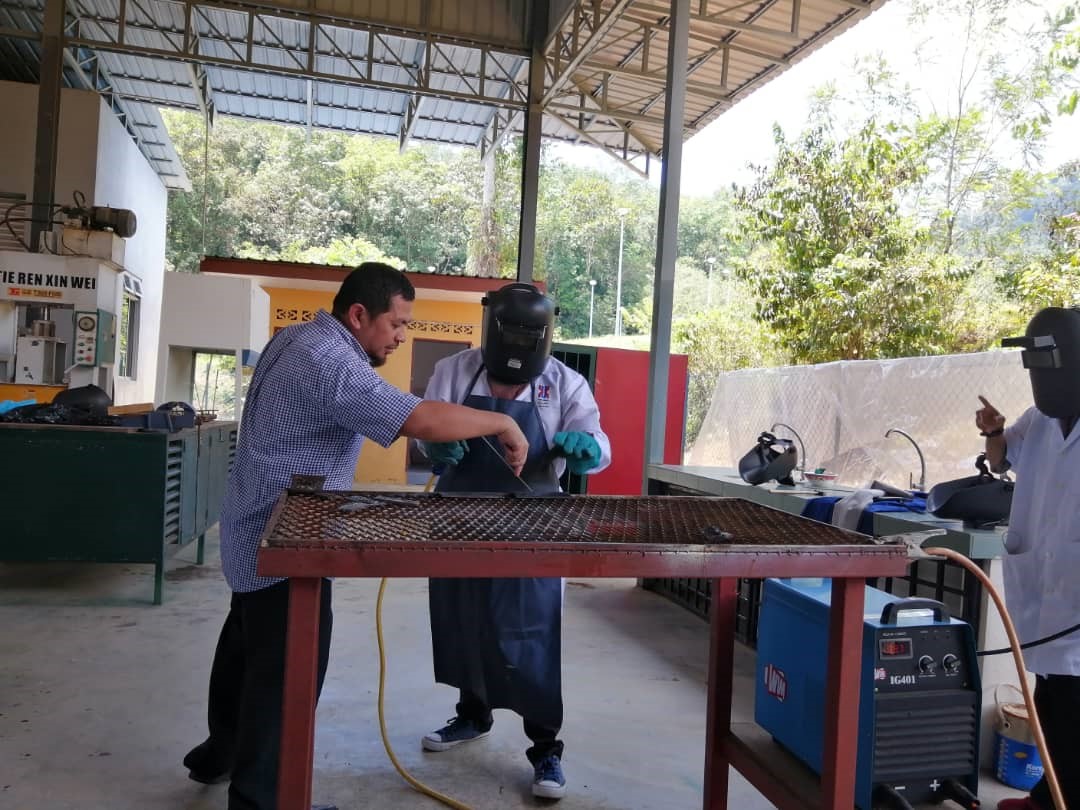
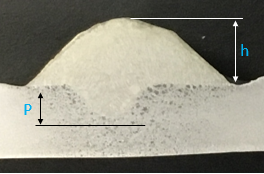
Since the heat treatment is a process of heating and cooling of the metal, in this lecture, the heat treatment is applied to low alloy carbon steel. Welding technique is used as a tool to heat the sample as shown in Figure (a) and (b). Welding process involves the temperature which is higher than melting point of carbon steel. Thus, steel will fuse or melt at the area covered by the welding arc. Meanwhile, the un-fuse area next to the fusion area and is affected by heat, termed as heat affected zone (HAZ). During this lecture, the students will study the formation of microstructure at this area. The variation of microstructure with different grain size formed as a result of the difference of achievable temperature and cooling rate during cooling process gives an interesting learning experience to the students. Prior to microstructure observation, students need to perform grinding and polishing, accompanied with etching (Nital solution as etchant), as shown in Figure (c). Subsequently, the microstructures are observed by using optical microscopy, as shown in Figure (d).
Article and Photo: Dr Sarizam Mamat





/alumni.png)